U.S. State Department Announcements on Peace Deals in July and August
From July 19 to August 7, 2025, the U.S. Department of State released statements supporting three key developments in conflict resolution across Southeast Asia and Africa.
GLOBAL — From July 19 to August 7, 2025, the U.S. Department of State released statements supporting three key developments in conflict resolution across Southeast Asia and Africa.
These encompassed a ceasefire between Cambodia and Thailand, a declaration of principles toward a peace agreement in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) involving rebel groups, and progress in implementing a prior peace agreement between the DRC and Rwanda. These efforts underscore U.S. diplomatic priorities in fostering regional stability through multilateral and bilateral engagements.
The peace deals were made via coordinated actions, including hosting meetings and facilitating oversight mechanisms. Analysis suggests a strategic emphasis on immediate halts to violence paired with long-term frameworks for economic cooperation and security coordination.
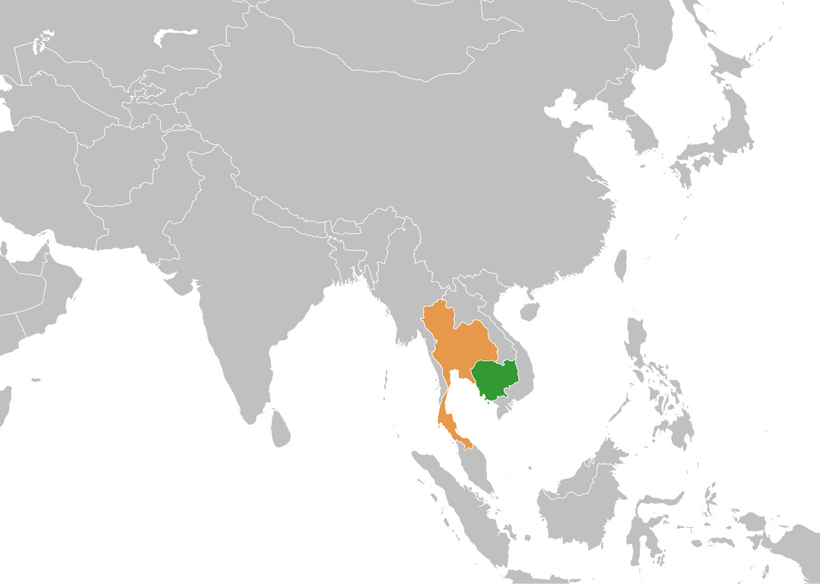
Cambodia-Thailand Ceasefire: Background and Developments
The border dispute between Cambodia and Thailand traces back to colonial-era treaties between France and Siam in 1904 and 1907, which ambiguously defined boundaries. Tensions centered on the Preah Vihear temple, awarded to Cambodia by the International Court of Justice in 1962, but the surrounding areas remained contested.
Clashes intensified in 2008 following Cambodia's UNESCO World Heritage listing of the temple, leading to military confrontations until a 2011 court order for troop withdrawal. The 2025 escalation revived these historical grievances, prompting renewed diplomatic intervention.
On July 28, 2025, the U.S. applauded the ceasefire declaration announced in Kuala Lumpur, committing to an immediate halt in violence and urging both nations to uphold their pledges. Gratitude was expressed to Malaysian Prime Minister Anwar Ibrahim for hosting the talks, with the U.S. pledging continued engagement in the process.
An update on August 7, 2025, welcomed the General Border Committee meeting as a step toward solidifying the ceasefire and establishing an ASEAN observation mechanism. Expectations were reiterated for full commitment to ending the conflict, acknowledging Malaysia's role in the July 28 special meeting co-organized with the United States.
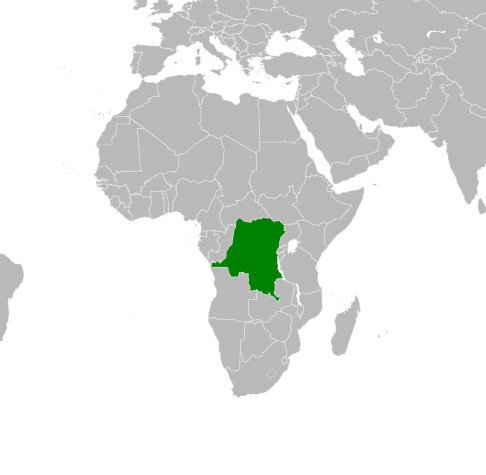
Declaration of Principles in the Democratic Republic of the Congo: Background and Developments
The conflict in eastern DRC involving the March 23 Movement (M23) and allied groups has roots in the 1994 Rwandan genocide spillover, with ethnic tensions and resource disputes fueling instability since the late 1990s. M23 was formed in 2012 from army deserters claiming the government failed to honor a 2009 peace accord integrating former rebels.
The group re-surged in 2022, capturing territories amid accusations of external support, leading to widespread displacement and human rights concerns.
On July 19, 2025, the U.S. welcomed the signing of a declaration of principles between the DRC government and representatives of the Congo River Alliance, M23, and Forces Armées Congolaises Indépendantes (FACI). This was viewed as progress toward a comprehensive peace agreement, with the U.S. affirming its dedication to advancing such diplomatic initiatives.
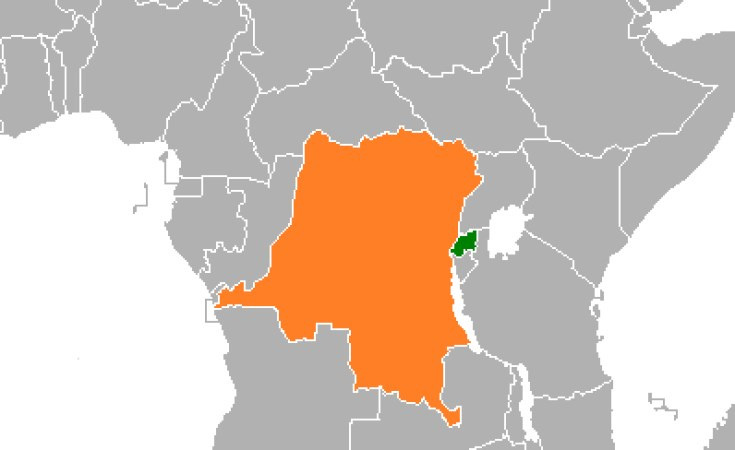
Implementation of DRC-Rwanda Peace Agreement: Background and Developments
Relations between the DRC and Rwanda have been strained since the 1994 genocide, when perpetrators fled to eastern DRC, prompting Rwandan invasions in 1996 and 1998 that ignited the First and Second Congo Wars, involving multiple nations and causing millions of deaths.
Ongoing accusations include Rwandan backing of rebels like M23 against Hutu militias, exacerbating ethnic violence and resource exploitation in the region.
Following the June 27, 2025, peace agreement signed in Washington, D.C., the U.S. hosted meetings from July 30 to August 1, 2025, to advance security and economic components. Representatives initialed the Regional Economic Integration Framework Tenets, addressing energy, infrastructure, mining, tourism, and health cooperation to promote prosperity.
The inaugural Joint Oversight Committee meeting on July 31 appointed chairpersons, established terms, and prepared for security coordination, observed by international partners. These steps were highlighted as advancing long-term stability in the Great Lakes region, with the U.S. committed to supporting progress toward a heads-of-state summit.